The CDC (Centers for Disease Control and Prevention) notes:
“What are some risk factors for choking?
Eating while talking or laughing, or eating too fast
Medical conditions, such as neurological or muscular disorders that affect the person’s ability to chew and swallow
Dental problems or poorly fitting dentures that affect the person’s ability to chew food properly”
What foods and objects can be choking hazards for children younger than 4 years?
Small foods, such as nuts, seeds and popcorn
Round, firm foods, such as hot dogs, grapes and hard candies
Sticky foods, such as peanut butter, chewing gum and gummy candies
Large foods that break easily into small pieces, such as teething biscuits and cookies
Chunked foods, such as fruit, raw vegetables, and meat or cheese
Small, round objects such as coins, buttons, button batteries, magnets, beads and vitamins
Small metal or plastic items such as toys, jewelry, safety pins, pen or marker caps and the pull tabs from soda cans
Plastic bags and deflated or broken balloons
Baby powder”
– – – – – – – – – – – – –
A bag of popcorn you buy could say on the bag:
“CHOKE WARNING: Do not give to children younger than 4 years old.”


The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) lists these
Potential Choking Hazards for Young Children
Fruits/Vegetables
• Cooked or raw whole corn kernels
• Uncut cherry or grape tomatoes
• Pieces of hard raw vegetables or fruit, such as raw carrots or apples
• Whole pieces of canned fruit
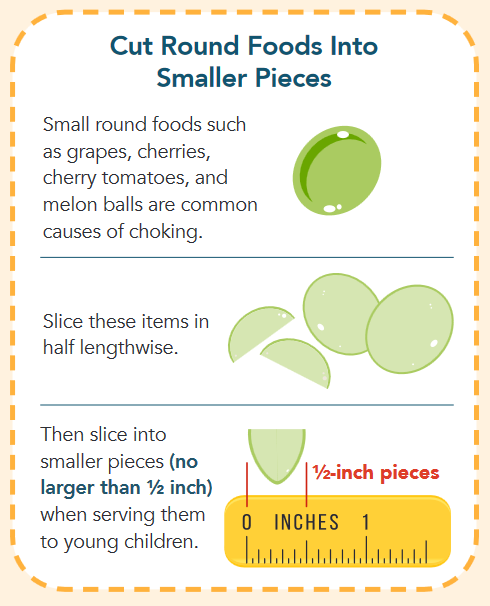
• Uncut grapes, berries, cherries, or melon balls
• Uncooked dried vegetables or fruit, such as raisins
Proteins
• Whole or chopped nuts and seeds
• Chunks or spoonfuls of nut and seed butters, such as peanut butter
• Tough or large chunks of meat
• Hot dogs, meat sticks, or sausages
• Large chunks of cheese, especially string cheese
• Bones in meat or fish
• Whole beans
Grain Products
• Cookies or granola bars
• Potato or corn chips, pretzels, popcorn, or similar snack foods
• Crackers or breads with seeds, nut pieces, or whole grain kernels
• Whole grain kernels of cooked barley, wheat, or other grains
• Plain wheat germ
Sweetened Foods
• Round or hard candy, jelly beans, caramels, gum drops, or gummy candies
• Chewy fruit snacks
• Chewing gum
• Marshmallows
The Resuscitation Council UK notes “Following successful treatment for choking, foreign material may nevertheless remain in the upper or lower respiratory tract and cause complications later. Victims with a persistent cough, difficulty swallowing, or with the sensation of an object being still stuck in the throat should therefore be referred for a medical opinion.”
The CDC (Centers for Disease Control and Prevention) warns:
“About 50,000 young children end up in emergency rooms each year
because they got into medicines while an adult wasn’t looking.
These emergency visits can be prevented by always putting every medicine up and away and out of children’s reach and sight every time you use it.”
The Red Cross warns: “Keep all poisonous substances out of reach of children or in drawers and cabinets with safety latches or locks. Some common poisonous substances inside and around the home include alcohol, drugs, medicines, vitamins, lighter fluid, lamp oil, hair and beauty products, baby oil, tobacco, cleaning products, paints, bug and weed killers and car products.”

And perhaps also of interest:
Helping Children Cope with Disaster
Babysitter Consent and Contact Form is for parents to fill out and leave with the babysitter or designated caregiver ( including relatives who might not be fully aware of current health issues for your child).
– – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – –
Note to on-line users not in my classes: this is a study sheet. It is not complete instruction in first aid or the topic named in the webpage title.
The author of this webpage, (written as a homework reading assignment for my students), does not give any warranty, expressed or implied, nor assume any legal liability or responsibility for the accuracy, completeness, or usefulness of any information, product, or process included in this website or at websites linked to or from it. Users of information from this website assume all liability arising from such use.
– – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – –