
In studies in the United States the CDC (Centers for Disease control) found that many people
do not know the symptoms of a heart attack and what to do.
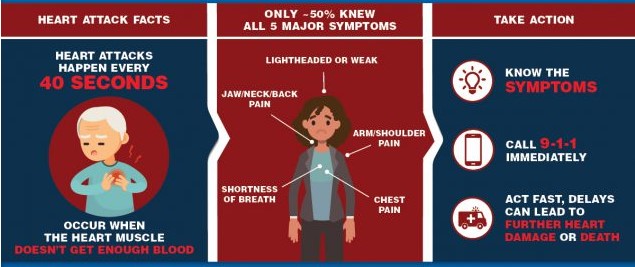
The CDC says:
“The major symptoms of a heart attack are
Chest pain or discomfort. Most heart attacks involve discomfort in the center or left side of the chest that lasts for more than a few minutes or that goes away and comes back. The discomfort can feel like uncomfortable pressure, squeezing, fullness, or pain.
Feeling weak, light-headed, or faint. You may also break out into a cold sweat.
Pain or discomfort in the jaw, neck, or back.
Pain or discomfort in one or both arms or shoulders.
Shortness of breath. This often comes along with chest discomfort, but shortness of breath also can happen before chest discomfort.
Other symptoms of a heart attack could include unusual or unexplained tiredness and nausea or vomiting. Women are more likely to have these other symptoms.”
The CDC notes:
Call 9-1-1 if you notice symptoms of a heart attack.
If you notice the symptoms of a heart attack in yourself or someone else, call 9-1-1 immediately. The sooner you get to an emergency room, the sooner you can get treatment to reduce the amount of damage to the heart muscle. At the hospital, health care professionals can run tests to find out if a heart attack is happening and decide the best treatment.
In some cases, a heart attack requires cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) or an electrical shock (defibrillation) to the heart to get the heart pumping again. Bystanders trained to use CPR or a defibrillator may be able to help until emergency medical personnel arrive.
Remember, the chances of surviving a heart attack are better the sooner emergency treatment begins.
Heart disease is the leading cause of death in the United States.
Heart attacks (also known as myocardial infarctions) occur when a portion of the heart muscle does not receive adequate blood flow, and they are major contributors to heart disease.
Early intervention is critical for preventing mortality in the event of a heart attack.
Identification of heart attack signs and symptoms by victims or bystanders,
and taking immediate action by calling emergency services (9-1-1),
are crucial to ensure timely receipt of emergency care and thereby improve the chance for survival
As a preview and/or review about the basics about heart attack and cardiac arrest,
Try to see if you can answer these questions:
“What are the signs and symptoms of a heart attack?”
“What are some reasons people might delay seeking medical attention when they are experiencing signs and symptoms of a heart attack?”
“What is the difference between a heart attack and cardiac arrest?”
Although a heart attack can lead to cardiac arrest, the two conditions are different. “In addition
to cardiovascular disease, what are some other causes of cardiac arrest?”
“What are the six links in the Adult Cardiac Chain of Survival?”
Why is it important to call 9-1-1 or the designated emergency number as soon as signs
and symptoms of heart attack are recognized?”
Give yourself a moment to think about each question, then scroll down past these photos of the Outdoor Club trip to Grand Teton National Park, to find the correct answers.



Here are the questions with the answers:
“What are the signs and symptoms of a heart attack?”
Chest pain, discomfort, pressure, heaviness or squeezing that lasts longer than 3 to 5 minutes and is not relieved by resting, changing position or taking medication, or that goes away and then comes back
Isolated, unexplained discomfort or pain that spreads to one or both arms, the back, the shoulder, the neck, the jaw or the upper part of the stomach
Dizziness or light-headedness
Trouble breathing, including noisy breathing, shortness of breath and breathing that is faster than normal
Nausea or vomiting
Pale or ashen (gray) skin
Sweating
A feeling of anxiety or impending doom
Extreme fatigue
Unresponsiveness
■ People may experience the signs and symptoms of a heart attack differently.
■ Not everyone will have every sign or symptom.
■ People who have had a heart attack before may not experience the same signs and symptoms if they have a second heart attack.
■ Men often have “classic” signs and symptoms of a heart attack, such as chest pain that radiates down one arm.
■ Women often experience milder chest pain or more general signs and symptoms, such as shortness of breath, nausea or vomiting, extreme fatigue, and dizziness or light-headedness.
“What are some reasons people might delay seeking medical attention when they are experiencing signs and symptoms of a heart attack?”
Lack of knowledge about, or failure to recognize, the signs and symptoms of a heart attack (symptoms can start slowly and persist for hours, days, or even weeks before a heart attack).
Denial or fear related to potentially having a life-threatening condition
Concerns about feeling foolish or embarrassed for seeking advanced medical care for a “false alarm”
Inadequate access to healthcare or a lack of healthcare insurance
“What is the difference between a heart attack and cardiac arrest?”
A heart attack occurs when blood flow to part of the heart muscle is blocked,
causing permanent damage to the heart muscle.
Cardiac arrest occurs when the heart stops beating or beats too ineffectively
to circulate blood to the brain and other vital organs.
Both a heart attack and cardiac arrest can happen at the same time, or they can be hours or days apart. Most heart attacks do not lead to cardiac arrest, but even if you are not sure if it is a heart attack, call 911 or your local emergency number.
Although a heart attack can lead to cardiac arrest, the two conditions are different. “In addition
to cardiovascular disease, what are some other causes of cardiac arrest?”
Breathing emergencies, such as drowning and choking.
Trauma (severe)
Electric shock
Drug overdose
“What are the six links in the Adult Cardiac Chain of Survival?”
The Cardiac Chain of Survival (as recognized by the Red cross and the American Heart Association) describes six actions, that when they are performed in rapid succession, increase a person’s chances of survival and recovery from cardiac arrest.
Recognition of cardiac arrest and activation of the EMS system
Early high quality CPR (cardiopulmonary resuscitation) with emphasis on chest compressions
Early, rapid defibrillation
Early advanced life support (Advanced resuscitation by Emergency Medical Services and other healthcare providers)
Integrated post-cardiac arrest care
Recovery with continued followup (including additional treatment, observation, rehabilitation, and psychological support)
Why is it important to call 9-1-1 or the designated emergency number as soon as signs
and symptoms of heart attack are recognized?”
Seeking advanced medical care as soon as the signs and symptoms of a heart attack are recognized
can minimize damage to the heart and may save the person’s life.
Remember that even though you need the consent of a sane, sober adult to give them care YOU DO NOT NEED consent to call 911,
and should call 911 if the person is experiencing signs and symptoms of a heart attack.
Do not drive the person yourself, or let them drive to the doctor/ emergency room.
The EMTs or Paramedics who arrive when you call 911 can start essential care before they get person to the emergency room,
sometimes saving their life on the drive there.
These acronyms are not mentioned in the text, but worth noting:
OHCA = out-of-hospital cardiac arrest
POHCA = pediatric out-of-hospital cardiac arrest
ROSC = return of spontaneous circulation
PICU = pediatric intensive care unit
T-CPR = Telecommunicator CPR
The American Heart Assn (AHA) reports: “When CPR begins prior to the arrival of emergency medical services (EMS) personnel, the person in cardiac arrest has a two to three-fold higher likelihood of survival. An effective way to ensure that CPR is provided quickly is for the emergency telecommunicators”. . .( the person who answers the phone when you call 911) . . . “to provide instant instructions with telecommunicator CPR (T-CPR). T-CPR allows bystander CPR to begin – it works by keeping the brain and heart alive until EMS arrives to provide defibrillation and other vital interventions. T-CPR can assist the untrained caller as well as remind the CPR trained caller how to provide high-quality CPR.”
T-CPR (Telecommunicator CPR) is also known as
DA-CPR (Dispatcher-Assisted Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation)
Please note that people in some other countries do CPR differently, such as starting with 5 rescue breaths instead of 1 or 2.
In other countries they often use different acronyms,
such as these from a Royal Lifesaving Society, New Zealand manual:
EAR – expired air resuscitation (rescue breathing)
ECC – external cardiac compression (EAR plus ECC = CPR)
and they refer to one operator and two operator CPR (one rescuer and two rescuer CPR)
– – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – –
CERP is not a different way of doing CPR, it refers to a Cardiac Emergency Response Plan (CERP), for example in a school.
Citizen CPR is not a different way of doing CPR, it has been described as “a system of care involving the entire community . . . fostering a culture of preparedness and response within communities.”
– – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – –
(Note to on-line users not in my classes: this is a study sheet. It is not complete instruction in first aid or the topic named in the webpage title.)
The author of this webpage, (written as a homework reading assignment for my students), does not give any warranty, expressed or implied, nor assume any legal liability or responsibility for the accuracy, completeness, or usefulness of any information, product, or process included in this website or at websites linked to or from it. Users of information from this website assume all liability arising from such use.
– – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – –